Constructing a Rain Garden: Benefits and How-To Guide. With a little ingenuity and a green thumb, you can transform your landscape into a beautiful, rainwater-diverting oasis that helps prevent erosion and supports biodiversity.
Here’s how to build your very own eco-friendly garden that embraces rainwater and nurtures the environmentBy building a garden that embraces rainwater and prevents erosion, you not only contribute to the health of your landscape but also play a part in conserving water and supporting biodiversity. Let your garden thrive as a testament to sustainable landscaping practices and responsible water management.
The Remarkable Advantages of Rain Gardens: A Green Solution for Urban Stormwater Management
Over the past few years, rain gardens have emerged as an innovative and effective remedy for addressing stormwater management issues in urban areas.
Grounded in scientific evidence, these eco-friendly spaces offer a multitude of benefits for both the environment and homeowners alike. Harnessing the power of nature, rain gardens have proven to be a go-to solution that tackles various environmental challenges while adding beauty and value to residential landscapes.
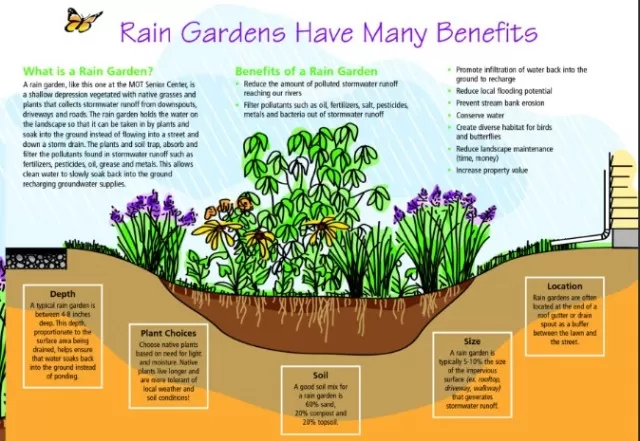
Mitigating Runoff and Preventing Flooding: One of the primary advantages of incorporating rain gardens into urban settings is their ability to effectively manage and control stormwater runoff.
Specifically designed to capture and absorb rainwater from impermeable surfaces such as roofs and driveways, rain gardens play a crucial role in alleviating the pressure on conventional stormwater systems. By doing so, they significantly reduce the risk of flooding and erosion during heavy rainfall, safeguarding homes and properties.
Enhancing Water Quality: Beyond managing runoff, rain gardens also act as natural filtration systems, enhancing the quality of water that eventually reaches streams, rivers, and other water bodies.
Through the deployment of carefully selected plants, these gardens effectively filter out pollutants and contaminants from rainwater as it seeps into the ground. This ecological purification process benefits not only the local environment but also the broader aquatic ecosystems.
Fostering Biodiversity and Encouraging Wildlife: An often-overlooked advantage of rain gardens is their role in promoting biodiversity and supporting various forms of wildlife.
These green havens become welcoming habitats for an array of organisms, including birds, butterflies, bees, and other beneficial insects. By incorporating native plant species, rain gardens attract essential pollinators, ensuring the perpetuation of plant life in the surrounding areas and contributing to the preservation of natural ecosystems.
Aesthetic Appeal and Environmental Consciousness: Aside from their functional benefits, rain gardens also contribute to the aesthetic appeal of urban landscapes.
By employing a diverse palette of native plants, flowers, and grasses, these gardens create visually captivating and harmonious Outdoor Spaces. Homeowners and communities can take pride in showcasing their commitment to environmental consciousness while simultaneously adding charm and uniqueness to their surroundings.
Erosion Prevention and Soil Stability: Rain gardens play an instrumental role in preventing soil erosion and maintaining the stability of the landscape.
By capturing and gradually releasing stormwater runoff, they act as natural buffers, dissipating the erosive force of water. Additionally, the roots of the carefully selected plant species firmly anchor the soil, reducing the risk of erosion and ensuring the long-term integrity of the land.
In conclusion, the advantages of rain gardens extend beyond their primary function as stormwater management tools.
These verdant oases offer an array of ecological benefits, ranging from mitigating runoff and improving water quality to fostering biodiversity and beautifying the urban environment. As the world increasingly seeks sustainable solutions to environmental challenges, rain gardens stand out as a shining example of how nature-inspired interventions can make a significant positive impact on both our surroundings and our lives.
Preparing for Building a Rain Garden: Key Steps for Success

Before embarking on the construction of a rain garden, it is essential to undertake thoughtful planning and preparation to ensure its functionality and longevity.
Here are some crucial steps to follow:.
Locate the Perfect Spot: Identifying the right location is fundamental to the success of your rain garden.
Observe the flow of water during rainfall to determine where runoff collects and how it moves across your yard. Ideally, position the rain garden in a natural drainage path.
If this is not feasible, consider redirecting runoff through swales or buried pipes leading to the rain garden. By understanding the water’s movement, you can optimize the rain garden’s effectiveness.
Test and Assess the Soil: The soil in your chosen location should possess good infiltration capabilities to allow rainwater to percolate into the ground efficiently.
Conduct a soil test to assess its composition and infiltration rate. A simple soil testing kit can help you evaluate essential parameters.
Ensure that the soil has adequate drainage capacity, as heavy clay soils might not be suitable for rain gardens. Perform a drainage test by digging a 1-foot deep and 1-foot diameter hole, filling it with water, and observing how quickly it drains.
If the water dissipates within 24 hours, the soil is suitable for a rain garden.
Plan for Overflow Management: A well-designed rain garden should include provisions for managing overflow.
Establish an inlet where runoff can flow into the basin and an overflow outlet to allow excess water to escape. This outlet can be a pipe or a notch in the berm to prevent flooding of the plants.
Proper overflow management ensures the rain garden remains functional during heavy rainfall events.
Carefully Consider Size and Contours: The size and shape of your rain garden will depend on the unique characteristics of your yard.
Analyze the topography and contours of the landscape to determine the most suitable size and shape for the rain garden. An appropriately planned rain garden will seamlessly blend into the surrounding environment, harmonizing with the aesthetics of your property.
For larger yards, consider creating a series of interconnected rain gardens to manage overflow effectively.
Select Resilient Plant Species: Choosing the right plant species is crucial for the success of your rain garden.
Opt for native plants that thrive in your area and can withstand both drought and occasional flooding. These plants have adapted to the local climate and will require minimal maintenance once established.
Avoid using seeds in the rain garden, as they may wash away during heavy rains. Instead, opt for growing plants with well-established root systems that can effectively control water flow.
Arrange the plants strategically, placing those most tolerant of standing water in the lower areas of the rain garden and taller plants toward the back to maintain visibility.
By following these essential steps and planning thoughtfully, you can create a beautiful and functional rain garden that effectively manages stormwater, supports local biodiversity, and adds value to your property.
Embrace the opportunity to contribute to a sustainable and eco-friendly approach to landscaping while enjoying the natural beauty and benefits of a well-designed rain garden.
Building a Rain Garden: Step-by-Step Guide
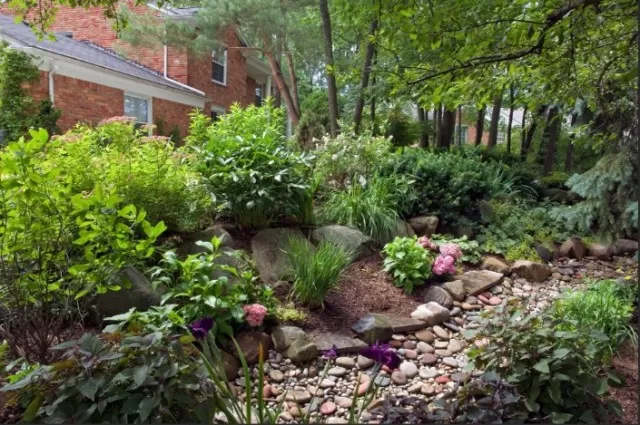

Constructing a rain garden involves careful planning and implementation to ensure its effectiveness and long-term success.
Follow these steps to bring your rain garden project to life:.
Call Dig Safe (811): Before beginning any excavation work, contact Dig Safe (811) or the appropriate utility locating service in your area.
This essential step ensures that the location of buried utility lines, such as gas, water, and electricity, is marked to avoid any accidental damage during the construction process.
Excavate the Rain Garden Basin and Drainage System: Using a skid steer, which can be rented from a construction rental store, or a garden shovel, start digging the rain garden basin to the desired depth and shape.
The basin will serve as the central area to collect and retain rainwater. Additionally, create a drainage system that redirects water from your downspouts, driveway, or other runoff sources into the rain garden.
Consider Ditches or Swales: Depending on your rain garden design and the need for water diversion, incorporate ditches or swales to facilitate the flow of runoff towards the rain garden.
These features can help hide any buried pipes and ensure that water efficiently reaches the rain garden.
Form Berms Around the Basin: If necessary, use the excavated soil to build berms around the rain garden basin.
Berms are raised areas that border the basin and help retain water on the lower edges of the rain garden, preventing excessive runoff.
Position the Inlet and Overflow Outlet: Properly place the inlet, which directs runoff into the rain garden, and the overflow outlet, which allows excess water to escape.
Careful positioning ensures that water flows efficiently through the rain garden, preventing waterlogging of plants.
Fill the Basin with Amended Soil: Add amended soil to fill the rain garden basin.
In some regions, you can find premixed “rain garden soil” designed specifically for this purpose. Alternatively, create a DIY mixture by combining 50 percent sand, 25 percent compost, and 25 percent topsoil to enhance the soil’s drainage capabilities.
Plant the Chosen Vegetation: Carefully plant the selected vegetation in the rain garden, taking into account their suitability for the local climate and their ability to tolerate both wet and dry conditions.
Opt for native plant species whenever possible, as they are well-adapted to the local environment.
Apply Shredded Hardwood Mulch: Spread a layer of shredded hardwood mulch, around two inches thick, over the soil surface in the rain garden.
This mulch helps suppress weed growth and retains moisture during dry periods, providing essential support to the newly planted vegetation. Hardwood mulch is less likely to wash away compared to softwood mulch.
Water the New Plants: During the first year, ensure that the newly planted vegetation receives regular watering to encourage robust root system development.
Adequate watering is crucial to help the plants establish themselves and thrive in their new environment.
By following these steps, you can successfully build a rain garden that effectively manages stormwater, supports biodiversity, and contributes to the overall health of the environment.
Remember to regularly maintain the rain garden to ensure its continued functionality and beauty for years to come.
*The information is for reference only.